Home » Travel Clinic » Altitude Sickness
Altitude Sickness
If you’re planning to travel to high-altitude destinations, altitude sickness can be an unexpected concern. At Periville Pharmacy, we provide trusted advice, prevention support, and altitude sickness medication to help you stay well and travel with confidence.
Based in Grimsby, with two branches on Cromwell Road and Wingate Road serving nearby areas including Laceby, Keelby, Great Coates, and Healing, our expert pharmacists are here to support you before and during your journey.


What Is Altitude Sickness?
Altitude Sickness Symptoms to Watch For
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
- Feeling sick or vomiting
- Extreme tiredness
- Dizziness or light-headedness
- Difficulty sleeping

What to Expect
at Your Appointment
- Private consultation with a pharmacist
- Assessment of your symptoms
- Clear recovery plan and guidance
What Causes Altitude Sickness?
- Altitude sickness is most likely when:
- You travel to high altitude too quickly.
- You don’t give your body time to acclimatise.
- You’ve had altitude sickness before.
- You become dehydrated or drink alcohol.
- Understanding these triggers is key to altitude sickness prevention and safer travel planning.
Altitude Sickness Treatment & Relief
- Pain relief such as paracetamol or ibuprofen.
- Anti-sickness medication.
- Preventive medication for those at higher risk.
- Guidance on when to descend or seek urgent medical care.
How to Prevent Altitude Sickness
- Ascend slowly and allow time to adjust.
- Take rest days during climbs.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Avoid alcohol.
- Avoid sleeping much higher than the previous night.
- Speak to a pharmacist before travel if you’ve had altitude sickness before.
Why Choose Periville Pharmacy?
- Expert travel health advice from trained pharmacists.
- Support with altitude sickness medication and prevention.
- Friendly, confidential consultations.
- Convenient local access across Grimsby and surrounding areas.
- Clear, practical advice tailored to your destination and travel pace.
Speak to Us Before You Travel
FAQs
News and Insights
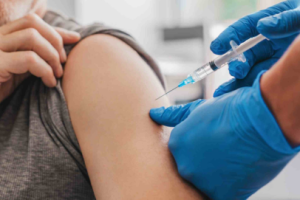
What Is the Difference Between the ACWY and B Meningitis Vaccines?
Meningitis is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection that affects the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Vaccination is the most effective way to reduce the risk of meningitis, but many people are unsure about the differences between the ACWY and B meningitis vaccines. Although both protect against

Can Typhoid Problems Cause Weight Gain or Loss?
Typhoid fever is a bacterial infection caused by Salmonella Typhi, often associated with contaminated food or water. Alongside the well-known symptoms such as high temperature and stomach discomfort, many people wonder whether typhoid can also lead to weight gain or weight loss. Can Typhoid Cause Weight Loss? Yes. Weight loss
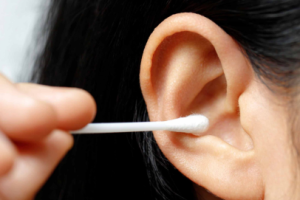
Can Earwax Build-Up Affect My Hearing?
Earwax may seem like a minor inconvenience, but excessive build-up can affect your hearing and overall ear health. While earwax plays a natural role in protecting the ear canal, too much of it can create problems. What Is Earwax and Why Do We Have It? Earwax (cerumen) is produced by